| Groove your brain! | ||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
Information  Bumpy Activity Book Bumpy Brains Activity Book |
 Cells of the Nervous System: Neurons Glial Cells |
|||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||
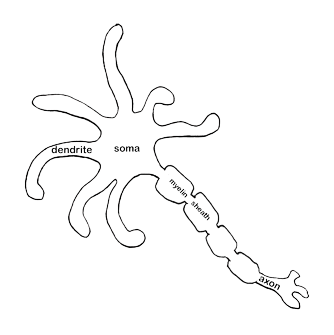
| The Structure of a
Neuron Guest starring Nestor the Neuron! |
||||||||||||||
|
Each part of Nestor has been
labeled. Below are the descriptions for his parts:
Soma (cell body): contains cytoplasm, the nucleus and other organelles such as mitochondria. Nucleus: contains DNA. Dendrites: receive information from other neurons (known as pre-synaptic neurons). Dendrites receive information through receptors. Receptors are also found on the cell body. Dendritic branch: a branching of the dendrite; also contains receptors. Axon hillock: connects the soma to the axon Axon: carries information to other neurons (known as post-synaptic neurons). Myelin
sheath: made up of lipids and proteins, myelin
electrically insulates the axon.
The purpose of myelin is to speed electrical impulses (information
being to sent
to post-synaptic neurons or other non-neuronal cell) down the axon.
Nodes
of Ranvier: gaps
between segments of myelin sheath. Electrical impulses jump from
one node to the next (over the fatty myelin sheaths), thus speeding the
impulse (this is called saltatory conduction).
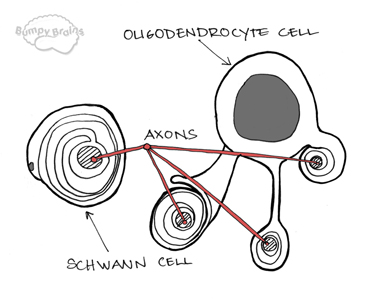
Schwann cell: in the peripheral nervous system, a type of glial cell that provides myelin to axons. In the central nervous system, oligodendrocytes provide myelin. Terminal button: also known as the axon terminal; the end of the axon. This is where the impulse finally ends and information is transmitted via the release of neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters: "chemical messengers" that allow neurons to communicate with each other. |
Neurons are
also known as
"brain cells," and are a type of cell that make up the nervous
system (along with glial cells).
They are responsible for everything we do, including
walking, talking, eating, sleeping, and thinking!
Neurons differ from other cells in the body because they have an axon and dendrites which allow them to send and receive information to and from other neurons. Note: the nervous
system is comprised of the central nervous
system (the brain and spinal
cord) and the peripheral nervous system (somatic and autonomic nervous
sytems).
 |
|||||||||||||
The Structure of a Neuron: Simplified by Vinny |
||||||||||||||
 |
|
|||||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||||||
|
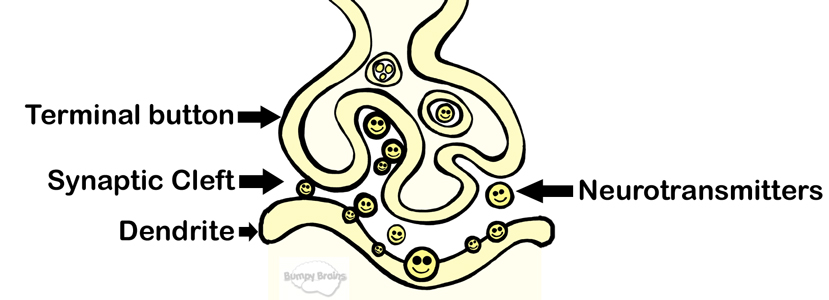
The Synapse |
||||||||||||||
A synapse is where a neuron communicates with a post-synaptic neuron or other non-neuronal cell. A synapse includes 3 parts:
|
 |
|||||||||||||
|
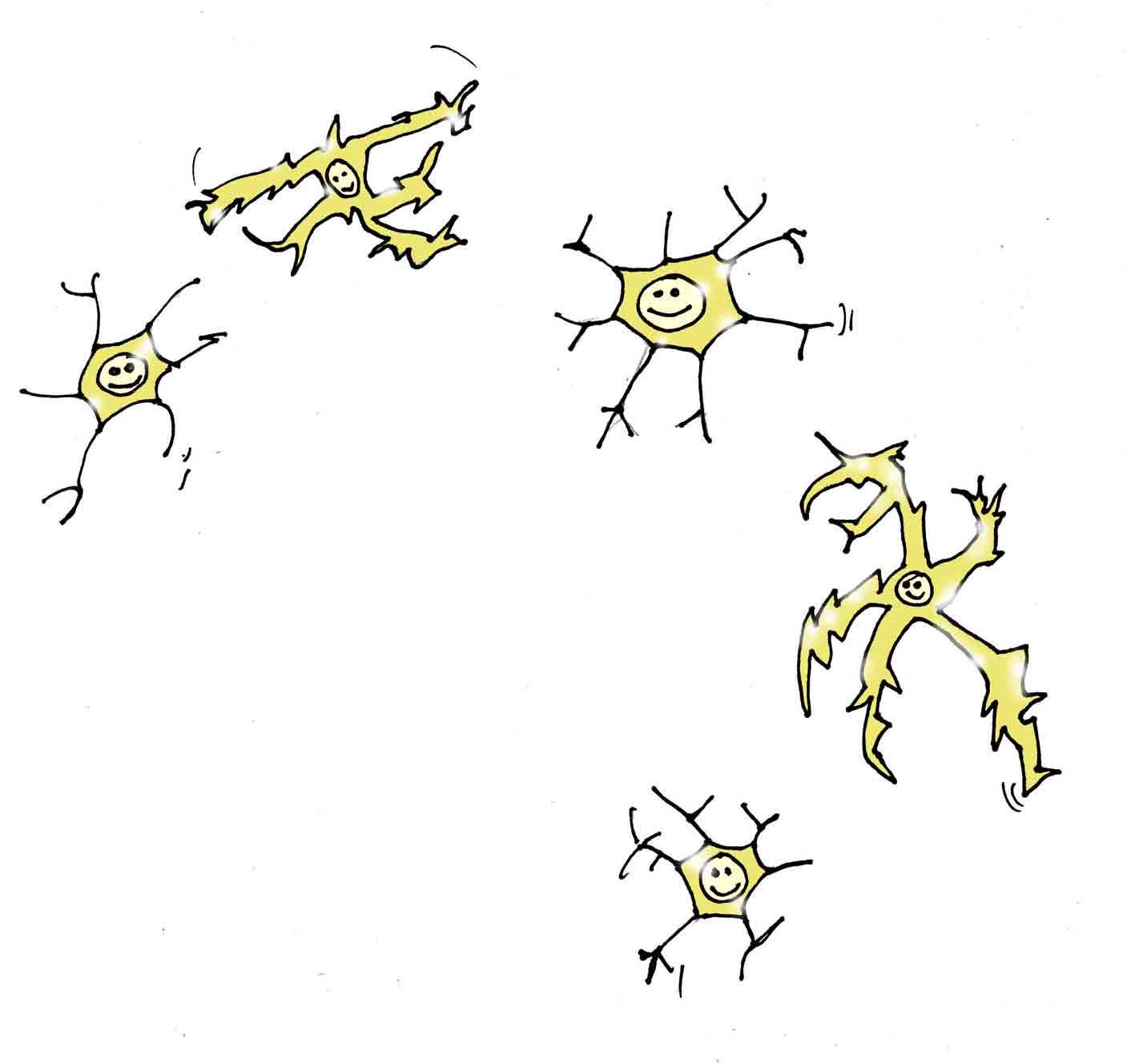
Glial Cells
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||